“We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze site traffic. By continuing to browse or closing this banner, you consent to our use of cookies. Read our Privacy Policy for more information.”
Blogs

India often celebrates topping global charts—but being called the “diabetic capital of the world” is no badge of honor. With over 77 million diagnosed diabetic patients and 25 million more pre-diabetic individuals, diabetes has reached near-endemic levels in the country.
Indians are more genetically and culturally predisposed to Type 2 diabetes than many other populations. This increased vulnerability stems from a mix of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Despite its growing prevalence, many people still ask: “What exactly is diabetes?”, “Why does it happen?”, or “Can it be prevented?” This article aims to answer those questions simply and clearly—because when it comes to health, knowledge is power.
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition in which the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels.
Glucose is the main energy source for our body and comes from the food we eat. To process glucose, our body uses insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. In diabetes, this process is disrupted—either due to insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively.
While some individuals show symptoms early, others may remain undiagnosed until complications occur. Common signs include:
Unchecked diabetes can damage almost every organ in the body. Major complications include:
Doctors use several tests for diagnosis:
| Test | Purpose |
| Fasting Blood Sugar Test | Measures blood sugar after overnight fasting |
| HbA1c Test | Shows average blood sugar over 2–3 months |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | Measures how your body processes glucose |
| Random Blood Sugar Test | Checks sugar levels regardless of last meal time |
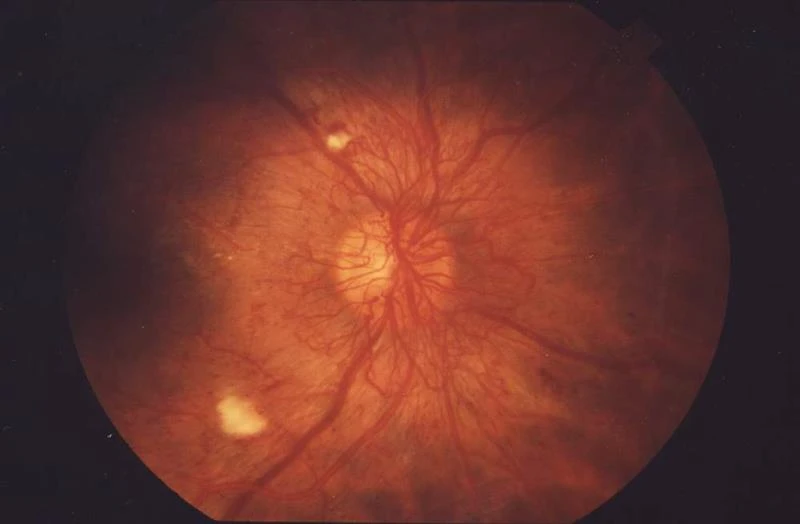
In addition to traditional tests, eye screening is emerging as a powerful early detection tool.
Diabetes can silently damage your eyes, often without early symptoms. That’s where fundus photography, enhanced with Artificial Intelligence (AI), comes in. This advanced technology captures high-resolution images of the back of the eye, allowing early diagnosis without the discomfort of traditional dilation drops.
Early detection through eye scans can prevent blindness and flag the onset of diabetes-related complications.
Diabetes doesn’t have to define your life. By being proactive, making healthy choices, and staying informed, you can prevent or manage the condition effectively.
Your health is in your hands. Act today, live better tomorrow.
“We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze site traffic. By continuing to browse or closing this banner, you consent to our use of cookies. Read our Privacy Policy for more information.”