“We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze site traffic. By continuing to browse or closing this banner, you consent to our use of cookies. Read our Privacy Policy for more information.”
Blogs
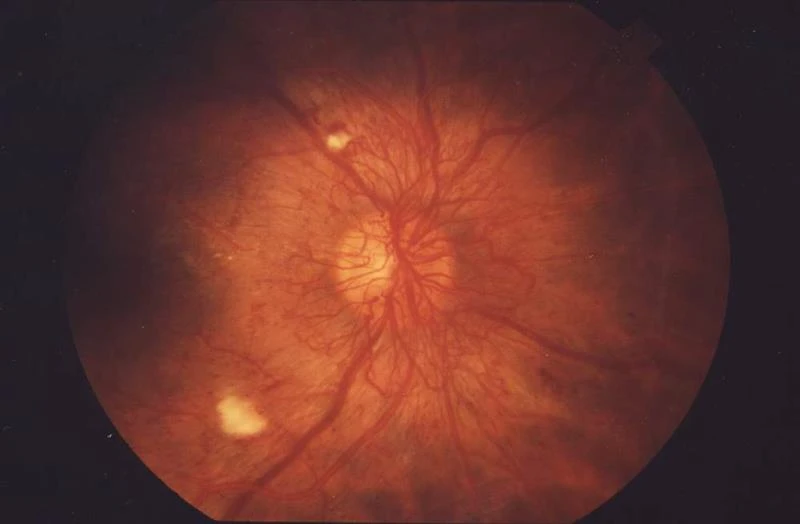
Diabetes is one of the most widespread chronic conditions globally—especially in India, where it affects millions across all age groups. But it’s not just high blood sugar levels that are concerning—it’s the serious complications that follow. One of the most dangerous, yet often overlooked, is Diabetic Retinopathy (DR), an eye condition that affects approximately 16.9% of diabetic individuals.
Fortunately, with modern eye scanning technology, early detection is now faster, simpler, and more accurate—offering hope and protection against vision loss.
Diabetic Retinopathy occurs when prolonged high blood sugar damages blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, these vessels may leak, swell, or close off. In advanced stages, abnormal new vessels may grow, leading to bleeding, scarring, and potential blindness.
Note: In early stages, there are often no symptoms at all—making regular eye screening essential for anyone with diabetes.
Eye scanning uses non-invasive, high-resolution imaging tools to capture detailed views of the retina, allowing early signs of damage to be spotted—often before you notice any change in vision.
According to international guidelines:
| Type of Diabetes | Recommended Screening Time |
|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | Within 5 years of diagnosis, then yearly |
| Type 2 Diabetes | At the time of diagnosis, then yearly |
| Diabetic Pregnant Women | Before pregnancy or during first trimester |
Tip: Your ophthalmologist may recommend more frequent exams based on your condition.
When caught early, diabetic retinopathy is far more treatable. Early detection allows:
Thanks to innovations in:
Diabetic eye care is becoming more accessible, even outside traditional eye clinics. Screenings can now happen in primary care clinics, pharmacies, or community health programs.
Note: Technology isn’t a replacement for care. Maintaining blood sugar levels and attending regular eye checkups is key.
If you or someone you love has diabetes, don’t wait for symptoms.
Your vision matters. Scan early. See clearly. Live fully.
This image highlights hallmark signs of diabetic retinopathy such as fluid leakage and vessel damage near the fovea—ideal for discussing early-stage pathology.

“We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze site traffic. By continuing to browse or closing this banner, you consent to our use of cookies. Read our Privacy Policy for more information.”